These stories highlight some of the work state Medicaid and Children’s Health Insurance Program (CHIP) agencies have done to improve tobacco cessation services. They showcase a variety of approaches to quality improvement (QI), including expanding coverage, enhancing quitlines, and offering incentives. Some states have also focused on specific populations, such as pregnant women and adults with behavioral health conditions. More state examples can be found in the tobacco cessation driver diagram and change idea table.
For more information on these materials and other QI technical assistance, email MedicaidCHIPQI@cms.hhs.gov.
State Stories: Short Videos and Examples
The Centers for Medicare & Medicaid Services (CMS) developed this series of brief videos to highlight successful tobacco cessation programs and strategies. Some programs specifically focus on populations at high risk for tobacco use, and most strategies include collaborating with QI partners. The videos include steps that Medicaid and CHIP agencies can take to integrate strategies into their state programs.
Video| Transcript: State Story—Oregon Quit Tobacco in Pregnancy (QTiP) Program
Financial and nonmonetary incentives are often used to encourage, reinforce, and sustain behavioral change for people who smoke. This brief video provides an overview of the QTiP program in Lane County, Oregon, which helps pregnant and postpartum women enrolled in Medicaid and CHIP to quit smoking.
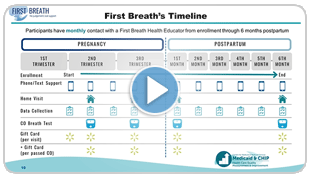
Video | Transcript: State Story—Wisconsin First Breath Program
This brief video discusses Wisconsin’s First Breath program and its multipronged approach to providing tobacco cessation support to during pregnancy and the postpartum period. The program features the use of intensive counseling services, self-help materials, and incentives and gifts for participants. First Breath staff share lessons learned from the first years of the program and the program improvements made in response.
Video | Transcript: State Story—Improving Tobacco Cessation Among Adults with Serious Mental Illness in Michigan
This brief video gives an overview of Michigan’s Region 10 Prepaid Inpatient Health Plan performance improvement project, which successfully increased the use of tobacco cessation resources for adults with serious mental illness.
For more information on these stories and on QI technical assistance, please email MedicaidCHIPQI@cms.hhs.gov.
Maryland’s Tobacco Quitline
Obtaining federal Medicaid funding for quitlines varies from state to state. Maryland’s Department of Health and Mental Hygiene, which includes the state public health and Medicaid programs, was one of the first state agencies to obtain approval for a cost allocation plan to claim a federal Medicaid administrative match for quitline activities. Medicaid’s partnership with the public health agency to support the quitline has led to better cessation services for Medicaid enrollees, improved sustainability for the quitline, and a demonstrated model of third-party reimbursement.
The Maryland Tobacco Quitline serves both Medicaid and non-Medicaid populations. The Maryland Medicaid agency and the state tobacco quitline collaborated to develop and submit a cost allocation plan to CMS to obtain reimbursement for quitline services for Medicaid members using an administrative match. When calling the quitline, individuals are asked about their insurance status and the name of their insurance carrier. The state compiles monthly client use data based on an intake survey conducted when callers initiate service. Allowable reimbursement includes a 50 percent match of counseling expenditures for Medicaid callers, who make up about 30 percent of quitline users.
From July 2011 through June 2012, Maryland served 2,108 Medicaid participants through the state quitline and has submitted administrative claims for $161,542.55. This support came at a critical time for the quitline, as the overall call volume grew from 14,132 inbound calls in state fiscal year 2011 to 18,590 inbound calls in state fiscal year 2012.
For more information on this story and on QI technical assistance, please email MedicaidCHIPQI@cms.hhs.gov.
Cessation Benefit Produces High Return on Investment in Massachusetts
Massachusetts implemented a highly effective smoking cessation program, including a medical cessation benefit based on the 2008 United States Public Health Service Clinical Practice Guideline Treating Tobacco Use and Dependence. The program removed barriers to access and encouraged benefit utilization by providing broad coverage for evidence-based tobacco cessation treatments. It also included an innovative service delivery component, with widespread communications and a promotional campaign directed at Medicaid consumers and clinicians.
Over the first two and a half years of the program, 37 percent of Massachusetts Medicaid enrollees who smoked used the benefit, and the prevalence of smoking among adult Medicaid members in Massachusetts fell from 38 percent to 28 percent.
Reports on health outcomes showed:
- A 46 percent decline in hospitalizations for heart attacks
- A 49 percent decline in hospitalizations for other diagnoses of acute coronary heart disease
- A $2.12 return on investment within three years for every dollar spent on the program
For more information on this story and on QI technical assistance, please email MedicaidCHIPQI@cms.hhs.gov.